Which of the Following Actions Will Always Increase Voltage
The output voltage will. The voltages will just add so the total voltage will be 28Vac at 60Hz.

Applications Of Optimization Models For Electricity Distribution Networks Claeys 2021 Wires Energy And Environment Wiley Online Library
No change to the action potential.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)
. An axon that is more negative than the resting membrane potential is said to be _____. Increase amplitude of action potential. Which of the following will increase the stimulus intensity.
Add the water to the acid. Increasing the voltage resulted in which of the following. During which phase of an action potential are voltage-gated K channels open while voltage-gated Na channels are closed.
Capacitance is defined as the property of a circuit that. Opposes a change in current. Increase in the primary voltage.
An action potential requires _____. Local action in a dry-cell or lead storage battery is the process whereby ____. Which of the following actions will always decrease voltage.
An action potential requires the opening of Ca2 channels whereas a graded potential does not. Aids a change in voltage. Which of the following is a shared characteristic between a spiking neuron and a nonspiking neuron.
Increase frequency of action potential. A depolarizing response occurred at R1 and R3 and action potentials occurred at R2 and R4. High concentration of voltage-gated Na channels at the axon hillock b.
Which change will always result in an increase in the gravitational force between two objects. Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential. A Inner electrons are always present in the semiconductor.
The Hodgkin cycle c. An action potential was always seen at R1. Similar but tetrodotoxin had a greater effect.
An action potential is propagated without decrement whereas a graded potential decrements with distance. Voltage Regulation V 2 N L - V 2 F L 100 V 2 N L If the rated voltage is applied to the primary winding of the transformer the secondary voltage changes with the load current and power factor even the primary voltage is kept constant. If an increase in extracellular potassium hyperpolarizes a neuron which of the following would be correct.
Voltage-gated Na channels change shape and their activation gates open. During depolarization the inside of the cell becomes more and more electropositive until the potential gets closer the. Increasing resistance and decreasing current C.
Look at the example below. Both prevent the storage of energy. Identify the type of membrane potential that occurred at R1 R2 R3.
Sodium flows out of the cell. A graded potential down the entire length of the axon d. Describe what happened when you applied a moderate stimulus to the sensory receptor.
This phase is called the depolarization. Why does the threshold increase when the interval between the stimuli decreases. Decreasing resistance and increasing current B.
When mixing electrolyte which if the following precautions should always be observed. Which of the following statement is correct. Increasing the voltage resulted in which of the following.
A capacitor is a device that stores energy in aan. C Free electrons are always present in the semiconductor. Voltage-gated Na channels change shape and their inactivation gates close.
Voltage-gated sodium channels to open and sodium to flow with its electrochemical gradient. Increasing AC Voltage is the same as increasing DC voltage. Voltage-gated potassium channels open and some voltage-gated sodium channels inactivate.
Effects of lidocaine and tetrodotoxin were _____. Increasing the voltage resulted in which of the following. The connection of the generator loop to these segments is such that the output is always of the same polarity.
For an inductor the induced voltage VL always BLANK the current by 90 degrees. Aids a change in current. A small depolarizing response occurred at R1 with no depolarization recorded by downstream sensors.
Increasing the duration of the stimulus. Decreasing resistance and keeping current constant D. The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions.
Voltage-gated potassium channels remain open and some voltage-gated sodium channels inactivate. Multiple Choice Question MCQ of Electronics page-16. An action potential was always seen at R1.
D Inner and bound electrons are always present in the. An axon that is more negative than the resting membrane potential is said to be _____. Voltage-gated K channels change shape and their activation gates open.
Which of the following is not an advantage of using an auto transformer. Add the acid to the water. An action potential down the entire length of the axon e.
If an increase in extracellular. An action potential has a threshold whereas a graded potential is an all-or-none phenomenon. To increase the voltage we connect the AC voltages in series to get a higher output voltage.
B Bound electrons are always present in the semiconductor. Increasing resistance and keeping current constant. Use a heavy duty aluminum pail.
Decrease in the. Which of the following is the most common neuron type in humans. Voltage-gated Ca2 channels change shape and their activation gates open.
Potassium flows into the cell. These changes in voltage of windings are known as voltage regulation. The minimum voltage that is required to generate an action potential is called the _____.
No change to the action potential. Which of the following statements areis a reason brushes are usually made of carbon are. What is a common piece of test equipment used to increase the ac voltage slowly while monitoring the operation of the equipment being repaired.
Opposes a change in voltage. Voltage-gated sodium channels open and some voltage-gated potassium channels inactivate. Increasing the masses of the objects and increasing the distance between the objects decreasing the masses of the objects and decreasing the distance between the objects increasing the masses of the objects and decreasing the distance between the objects.
If the frequency of all the voltages are the same the magnitude of the voltages simply add.

Action Potentials Foundations Of Neuroscience

Introduction To Ideal Op Amp Circuit Characteristics

Action Potentials Foundations Of Neuroscience
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub

Digital To Analog Conversion An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Electrical Safety Applied Industrial Electricity

Action Potential Propagates An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
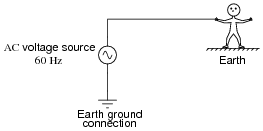
Electric Shock Worksheet Basic Electricity

Action Potentials Foundations Of Neuroscience
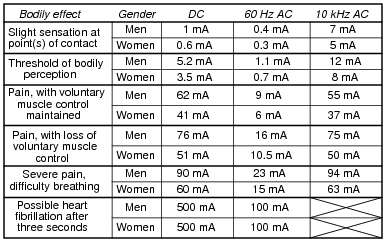
Electric Shock Worksheet Basic Electricity

Action Potentials Foundations Of Neuroscience

Electrical Safety Applied Industrial Electricity

Action Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
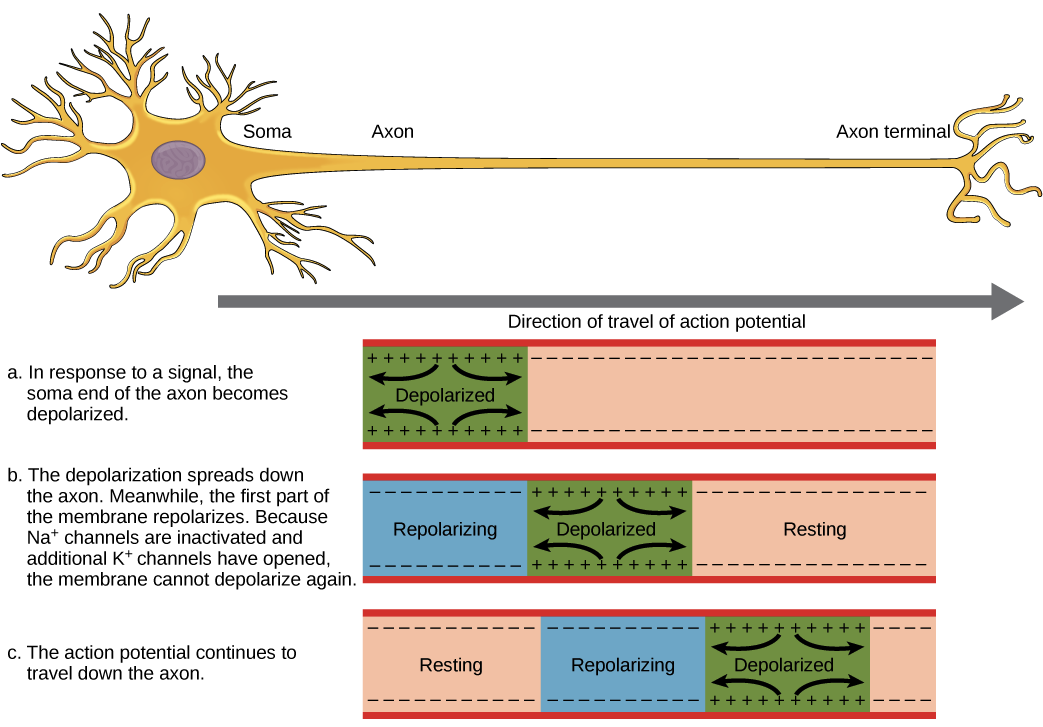
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy

Proportional Action An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
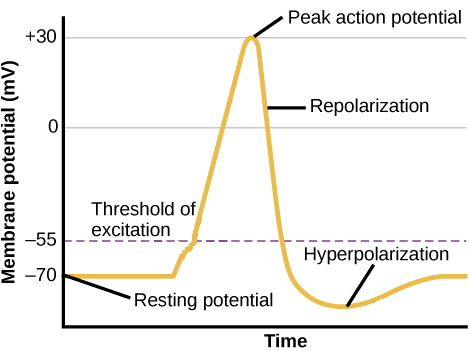
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy

Transformers Applied Industrial Electricity
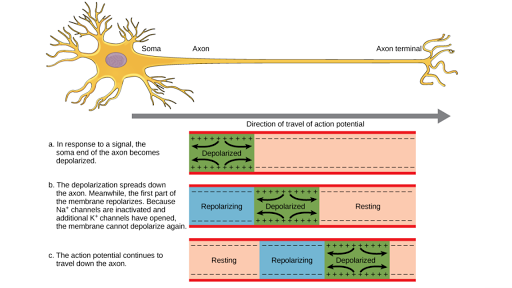
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy
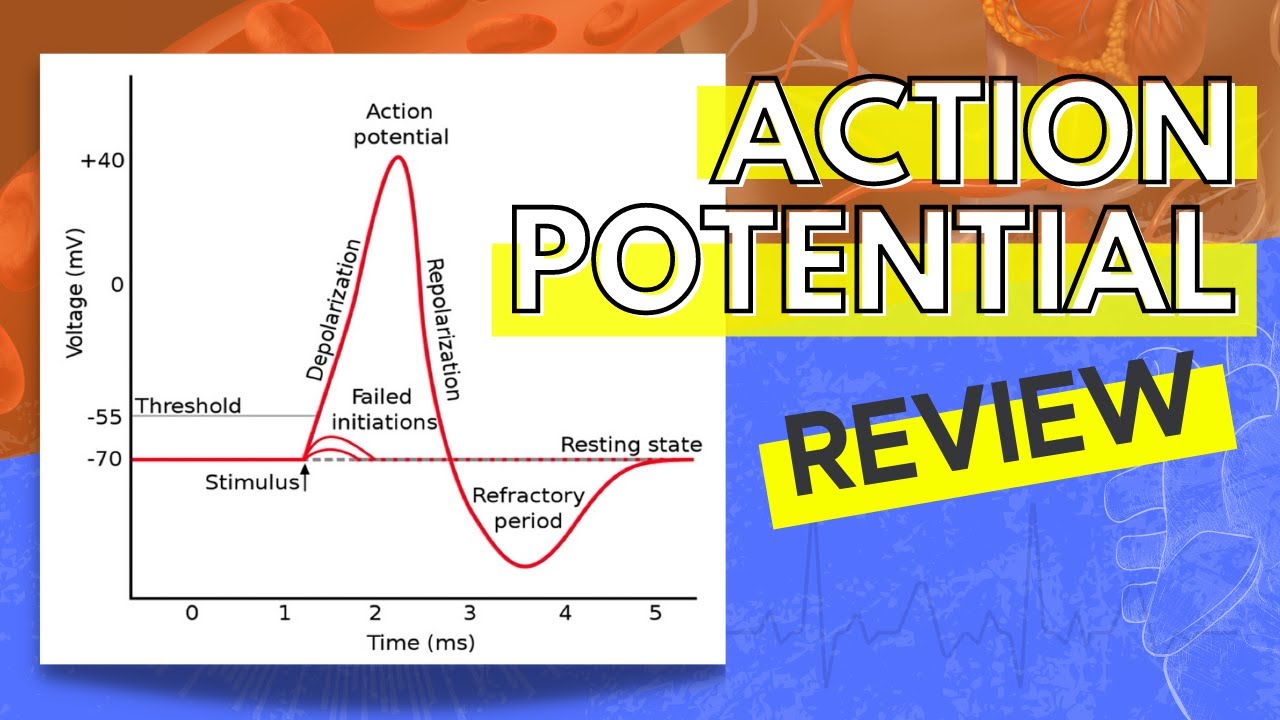
Comments
Post a Comment